Linux Development in Windows 10 with Docker and WSL 2
In this article we’ve learned how to set up a Linux development environment using Docker containers and WSL 2, with Windows 10 Pro. This is a nice approach for anybody who’s confortable on Windows and needs access to a Linux environment for development; and have that environment be easy to reproduce. The preferred choice for millions of developers that are building containerized apps. Docker Desktop is an application for MacOS and Windows machines for the building and sharing of containerized applications. Access Docker Desktop and follow the guided onboarding to build your first containerized application in minutes. Switch between Windows and Linux containers describes how you can toggle between Linux and Windows containers in Docker Desktop and points you to the tutorial mentioned above. Getting Started with Windows Containers (Lab) provides a tutorial on how to set up and run Windows containers on Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019.
I’m first and foremost a Windows guy. But for a few years now, moving away from working mostly with .NET and into a plethora of open source technologies has given me the opportunity to change platforms and run a Linux-based system as my daily driver. Ubuntu, which I honestly love for work, has been serving me well by supporting my development workflow with languages like PHP, JavaScript and Ruby. And with the help of the excellent Visual Studio Code editor, I’ve never looked back. There’s always been an inclination in the back of my mind though, to take some time and give Windows another shot.
With the latest improvements coming to the Windows Subsystem for Linux with its second version, the new and exciting Windows Terminal, and Docker support for running containers inside WSL2, I think the time is now.
In this post, we’ll walk through the steps I took to set up a PHP development environment in Windows, running in a Ubuntu Docker container running on WSL 2, and VS Code. Let’s go.
Note: You have to be on the latest version of Windows 10 Pro (Version 2004) in order to install WSL 2 by the usual methods. If not, you’d need to be part of the Windows Insider Program to have access to the software.
What’s new with WSL 2
This is best explained by the official documentation. However, being a WSL 1 veteran, I’ll mention a few improvements made which have sparked my interest in trying it again.
1. It’s faster and more compatible
WSL 2 introduces a complete architectural overhaul. Now, Windows ships with a full Linux Kernel which WSL 2 distributions run on. This results in greatly improved file system performance and much better compatibility with Linux programs. It’s no longer running a Linux look-alike, but actual Linux.
2. It’s better integrated with Windows
This is a small one: we can now use the Windows explorer to browse files within a WSL distribution. This is not a WSL 2 exclusive feature, it has been there for a while now. I think it’s worth mentioning though, because it truly is a great convenience and a far cry from WSL’s first release, where Microsoft specifically advised against manipulating WSL distribution file systems from Windows. If nothing else, this makes WSL feel like a first class citizen in the Windows ecosystem and shows that Microsoft actually cares about making it a good experience.
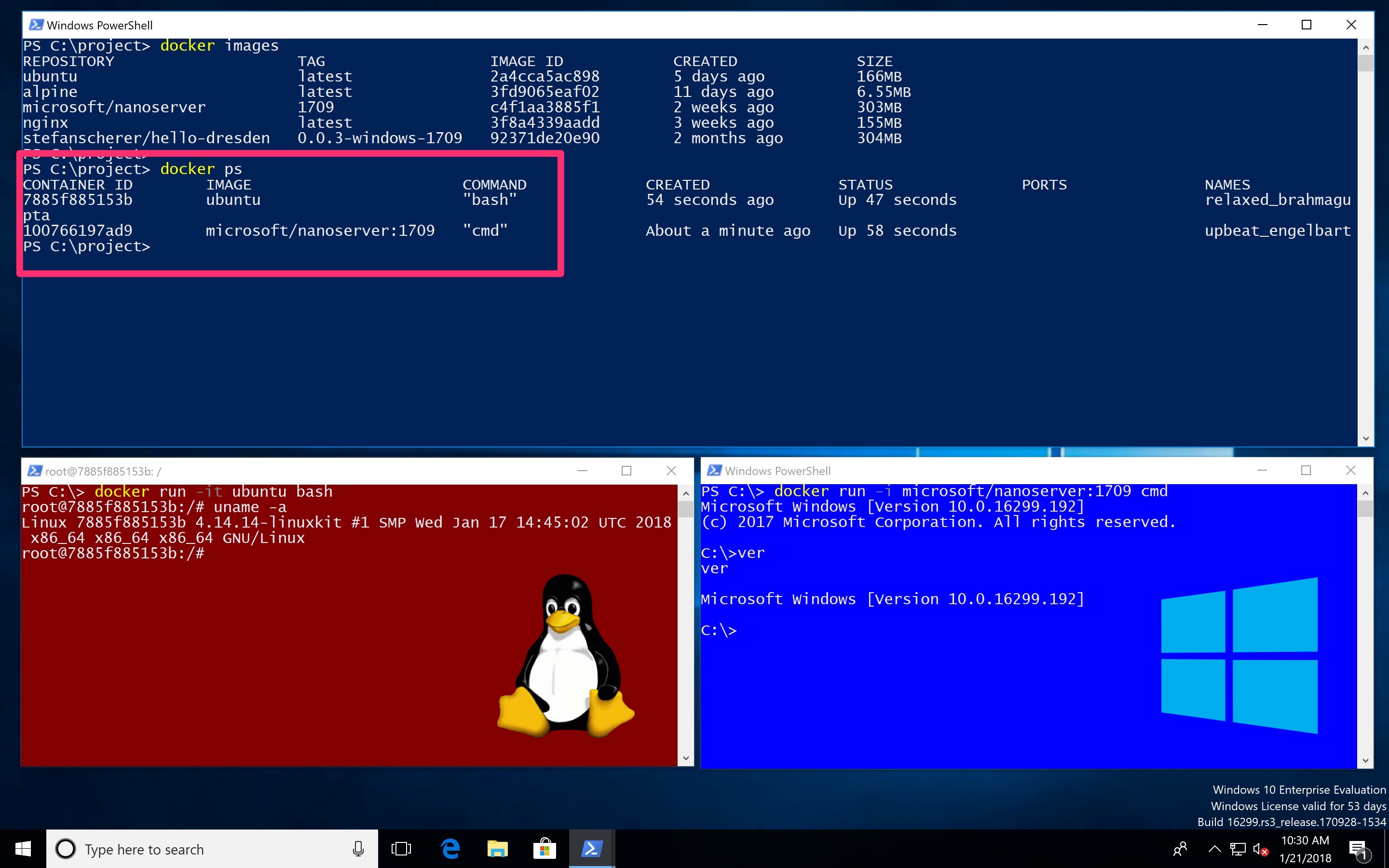
Docker Linux On Windows 10
3. It can run Docker
I’ve recently been learning more and more about Docker and it’s quickly becoming my preferred way of setting up development environments. Due to its lightweightness, ease of use, repeatability, and VM-like compartmentalization, I find it really convenient to develop against a purpose-built Docker container, rather than directly in my local machine. And with VS Code’s Remote development extension, the whole thing is very easy to set up. Docker for Windows now supports running containers within WSL, so I’m eager to try that out and see how it all works.
4. A newer version means several bugfixes
Docker Linux On Windows Server 2019
Performance notwithstanding, WSL’s first release was pretty stable. I did, however, encounter some weird bugs and gotchas when working with the likes of SSH and Ruby during certain tasks. It was nothing major, as workarounds were readily available. I’ve already discussed some of them here, so I won’t bother mentioning them here again. But thanks to the fact that the technology has matured since last time I saw it, and considering the architectural direction it is going in, I’m excited to not have to deal with any number of quirks.
The development environment
Ok, now with some of the motivation out of the way, let’s try and build a quick PHP Hello World app running in a Docker container inside WSL 2, make sure we can edit and debug it with VS Code, and access it in a browser from Windows.
Step 1: Install WSL 2 and Ubuntu
Step 1 is obviously to install WSL and a Linux distribution that we like. Microsoft’s own documentation offers an excellent guide on how to do just that. But in summary, we need to:
- Enable the “Windows Subsystem for Linux” and “Virtual Machine Platform” features by running these on an elevated PowerShell:
- Restart your machine.
- Set WSL 2 as the default version with:
wsl --set-default-version 2, also from PowerShell. - Install your desired distribution from the Microsoft Store. I chose Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
- After installing, open the “Ubuntu 20.04 LTS” app from the Start menu and it should come up with a command line console. Wait for it to finish installing. It should prompt for a username and password along the way. Choose something you won’t forget.
Optionally, you can install the Windows Terminal app to get a better command line experience. Windows Terminal can be used to interact with PowerShell and the classic CMD, as well as with our WSL distributions.
Step 2: Install Docker
Installing Docker is very straightforward. Just download the installer for Docker Desktop for Windows, execute it, and follow the wizard’s steps. Make sure that during setup the “Use the WSL 2 based engine” option is selected. In most cases, the installer will detect WSL 2 and automatically have the option selected.
Follow the official instructions for more details on the process, but it really is that simple.
Step 3: Install some useful VS Code extensions
Our objective is to create a new development environment inside a Docker container and connect to it directly with VS Code. To do that, we use a few useful extensions:
- The Docker extension which allows us to browse and manage images and containers and other types of Docker assets.
- The Remote - WSL extension which allows VS Code to connect to a WSL distribution.
- The Remote - Containers extension which allows VS Code to connect to a container.
Step 4: Create the development container
The extensions that we installed will allow us to use VS Code to work on code from within our WSL Ubuntu as well as from the container. Specifically, we want to connect VS Code to a container. There are a few ways to do this, but I will describe the one I think is the easiest, most convenient and “automagic” by fully leveraging the tools.
Let’s begin by opening a WSL Ubuntu terminal session, which will show something like this:
The project directory
Let’s change to our home, create a new directory for our new project, and change into it.
Because we installed the Remote - WSL extension, we can open up this directory in VS Code with code .. Opening a terminal (Ctrl + `) in this VS Code instance opens WSL console, not Windows.
The Dockerfile
Now let’s create a new file called Dockerfile which will define what our development environment image will look like. For a no-frills PHP environment, mine looks like this:
This script will later be used to create our development container. It will have PHP, Xdebug and Composer. This is all we need for our simple Hello World app. For more complex scenarios, other software like database clients or PHP extensions can be easily installed with additional RUN statements that call upon the apt package manager.
Consider reading through Docker’s official documentation on Dockerfiles to learn more.
The configuration file
Now, to leverage VS Code’s capabilities, let’s add a development container configuration file. In our current location, we need to create a new directory called .devcontainer and, inside that, a new file called devcontainer.json. I put these contents in mine:
A default version of this file can be automatically generated by running the “Remote-Containers: Add Development Container Configuration Files…” command in VS Code’s Command Palette (Ctrl + Shift + P).
The development container
Now that we have all that in place, we can create our image, run our container, and start coding our app. Bring up the VS Code Command Palette with Ctrl + Shift + P and run the “Remote-Containers: Reopen in Container” command. The command will:
- Read the Dockerfile and create an image based on that. This is like running
docker build -t AUTOGENERATED_IMAGE_ID . - Run a container based on that image with the settings specified in
.devcontainer/devcontainer.json. In our case, all it will do is enable the container’s port 5000 to be accessible by the host. This is more or less like running:docker run -d -p 5000:5000 -v ${PWD}:/workspaces/php-in-docker-demo AUTOGENERATED_IMAGE_ID - Open a new VS Code instance connected to the container with the
/workspaces/php-in-docker-demodirectory open.
It will take a while, but after it’s done, we will have a VS Code instance running directly in the container. Open the VS Code terminal with Ctrl + ` and see for yourself. It will show a prompt looking like this:
You can for example, run php -v in this terminal, and expect something along these lines:
This is PHP running, not in Windows, not in our WSL Ubuntu, but in the Docker container.
Hello Windows + WSL 2 + Ubuntu + Docker + PHP + VS Code

Let’s now create our app. Add a new index.php file containing something silly like:
Then, in the VS Code console (remember, Ctrl + `), start up an instance of the built in PHP development server wth php -S 0.0.0.0:5000. It’s important that we use port 5000 because that’s the one that we configured our container to use.
Docker Linux On Windows Host
Navigate to http://localhost:5000/ in your browser and feel good about a job well done.
Interactive debugging
When configuring our development container, we added Xdebug and the PHP Debug VS Code extension. This means that VS Code can leverage Xdebug to provide an interactive debugging experience for PHP code.
Almost everyting is set up at this point, we just need to do the usual VS Code configuration and add a launch.json file. To do so, in VS Code, press Ctrl + Shift + D to bring up the “Run” panel, click on the “create a launch.json file” link, and in the resulting “Select Environment” menu, select “PHP”.
After that, the “Run” panel will show a green triangular “Start Debugging” button next to a “Listen to XDebug” text. If you haven’t already, start up a dev web server with php -S 0.0.0.0:5000, click on the “Start Debugging” button, put a breakpoint somewhere in your index.php file, and finally open up http://localhost:5000/ in a browser.
We’re interactively debugging PHP code running on a Docker container in WSL from our Windows IDE/editor. Pretty cool, huh?
And that’s all for now. In this article we’ve learned how to set up a Linux development environment using Docker containers and WSL 2, with Windows 10 Pro. This is a nice approach for anybody who’s confortable on Windows and needs access to a Linux environment for development; and have that environment be easy to reproduce.
Resources:
Comments
 Visit theGitHub issueto view and write comments.
Visit theGitHub issueto view and write comments.Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Docker Desktop for Windows is the Community version of Docker for Microsoft Windows.You can download Docker Desktop for Windows from Docker Hub.
By downloading Docker Desktop, you agree to the terms of the Docker Software End User License Agreement and the Docker Data Processing Agreement.
System requirements
Your Windows machine must meet the following requirements to successfully install Docker Desktop.
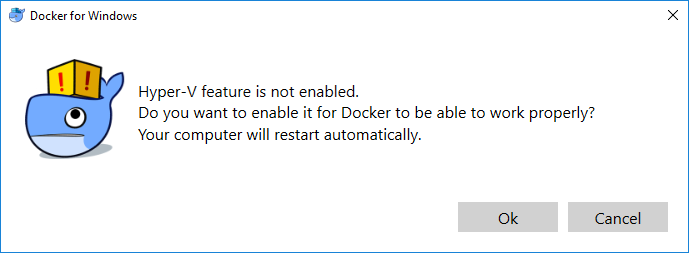
Hyper-V backend and Windows containers
Windows 10 64-bit: Pro, Enterprise, or Education (Build 17134 or higher).
For Windows 10 Home, see System requirements for WSL 2 backend.
- Hyper-V and Containers Windows features must be enabled.
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully run ClientHyper-V on Windows 10:
- 64 bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
- 4GB system RAM
- BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in theBIOS settings. For more information, seeVirtualization.
WSL 2 backend
- Windows 10 64-bit: Home, Pro, Enterprise, or Education, version 1903 (Build 18362 or higher).
- Enable the WSL 2 feature on Windows. For detailed instructions, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
The following hardware prerequisites are required to successfully runWSL 2 on Windows 10:
- 64-bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
- 4GB system RAM
- BIOS-level hardware virtualization support must be enabled in theBIOS settings. For more information, seeVirtualization.
- Download and install the Linux kernel update package.
Note
Docker supports Docker Desktop on Windows for those versions of Windows 10 that are still within Microsoft’s servicing timeline.
What’s included in the installer
The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine,Docker CLI client, Docker Compose,Notary,Kubernetes,and Credential Helper.
Containers and images created with Docker Desktop are shared between alluser accounts on machines where it is installed. This is because all Windowsaccounts use the same VM to build and run containers. Note that it is not possible to share containers and images between user accounts when using the Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend.
Nested virtualization scenarios, such as running Docker Desktop on aVMWare or Parallels instance might work, but there are no guarantees. Formore information, see Running Docker Desktop in nested virtualization scenarios.
About Windows containers
Looking for information on using Windows containers?
- Switch between Windows and Linux containersdescribes how you can toggle between Linux and Windows containers in Docker Desktop and points you to the tutorial mentioned above.
- Getting Started with Windows Containers (Lab)provides a tutorial on how to set up and run Windows containers on Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019. It shows you how to use a MusicStore applicationwith Windows containers.
- Docker Container Platform for Windows articles and blogposts on the Docker website.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows
Double-click Docker Desktop Installer.exe to run the installer.
If you haven’t already downloaded the installer (
Docker Desktop Installer.exe), you can get it from Docker Hub. It typically downloads to yourDownloadsfolder, or you can run it from the recent downloads bar at the bottom of your web browser.When prompted, ensure the Enable Hyper-V Windows Features or the Install required Windows components for WSL 2 option is selected on the Configuration page.
Follow the instructions on the installation wizard to authorize the installer and proceed with the install.
When the installation is successful, click Close to complete the installation process.
If your admin account is different to your user account, you must add the user to the docker-users group. Run Computer Management as an administrator and navigate to Local Users and Groups > Groups > docker-users. Right-click to add the user to the group.Log out and log back in for the changes to take effect.
Start Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop does not start automatically after installation. To start Docker Desktop, search for Docker, and select Docker Desktop in the search results.
Docker Run Linux On Windows
When the whale icon in the status bar stays steady, Docker Desktop is up-and-running, and is accessible from any terminal window.
If the whale icon is hidden in the Notifications area, click the up arrow on thetaskbar to show it. To learn more, see Docker Settings.
When the initialization is complete, Docker Desktop launches the onboarding tutorial. The tutorial includes a simple exercise to build an example Docker image, run it as a container, push and save the image to Docker Hub.
Congratulations! You are now successfully running Docker Desktop on Windows.
If you would like to rerun the tutorial, go to the Docker Desktop menu and select Learn.
Automatic updates
Starting with Docker Desktop 3.0.0, updates to Docker Desktop will be available automatically as delta updates from the previous version.
When an update is available, Docker Desktop automatically downloads it to your machine and displays an icon to indicate the availability of a newer version. All you need to do now is to click Update and restart from the Docker menu. This installs the latest update and restarts Docker Desktop for the changes to take effect.
Uninstall Docker Desktop
To uninstall Docker Desktop from your Windows machine:
- From the Windows Start menu, select Settings > Apps > Apps & features.
- Select Docker Desktop from the Apps & features list and then select Uninstall.
- Click Uninstall to confirm your selection.
Docker Linux On Windows Server 2019
Important
Docker Linux Container On Windows 10 Not Working
Uninstalling Docker Desktop destroys Docker containers, images, volumes, andother Docker related data local to the machine, and removes the files generatedby the application. Refer to the back up and restore datasection to learn how to preserve important data before uninstalling.
Where to go next
- Getting started introduces Docker Desktop for Windows.
- Get started with Docker is a tutorial that teaches you how todeploy a multi-service stack.
- Troubleshooting describes common problems, workarounds, andhow to get support.
- FAQs provide answers to frequently asked questions.
- Release notes lists component updates, new features, and improvements associated with Docker Desktop releases.
- Back up and restore data provides instructions on backing up and restoring data related to Docker.
